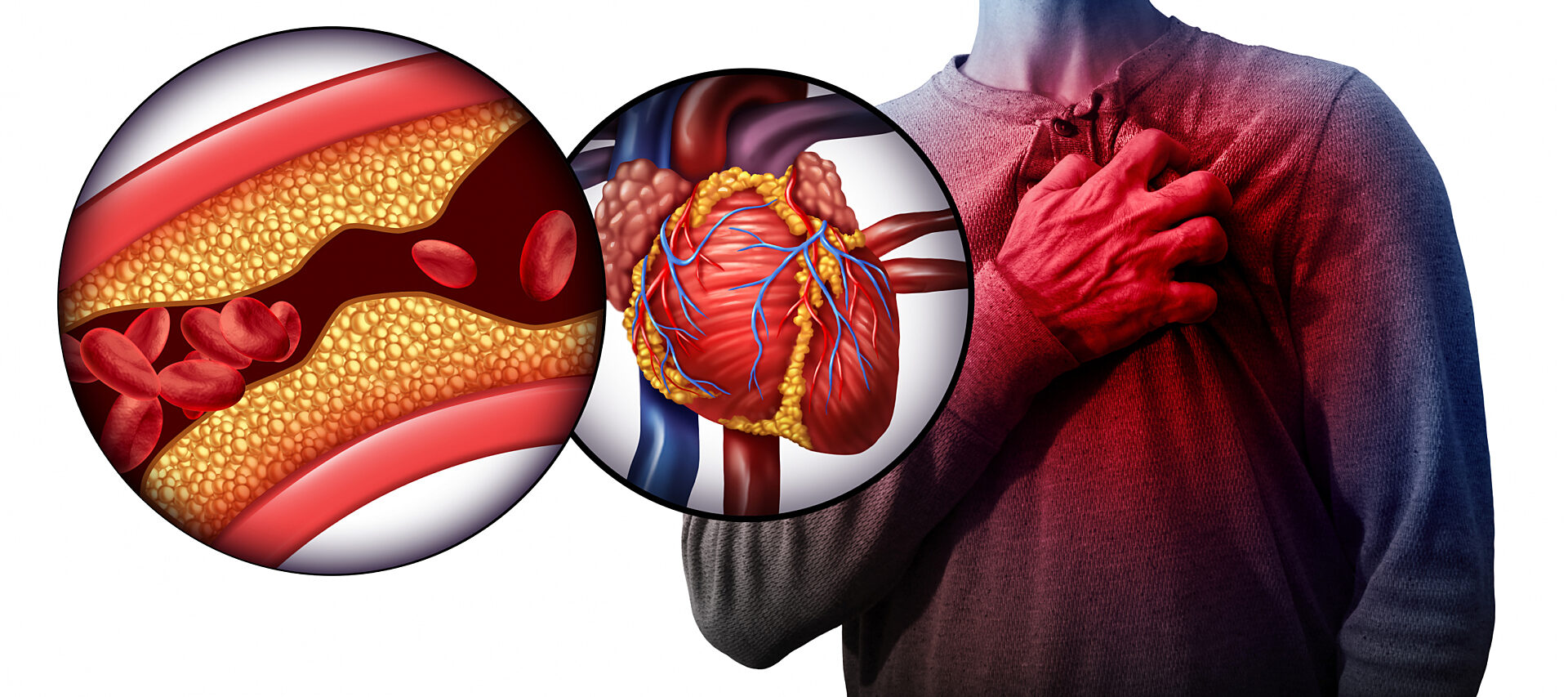
Experts warn that prolonged exposure to noise above 70 decibels can lead to serious health issues, including hearing loss and heart problems. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that residential areas should not exceed 55 decibels during the day.
Common Sources of Noise Pollution:
- Traffic and Industrial Activities: Areas with high traffic volume and industrial activities tend to have higher noise levels.
- Generators and Machinery: The use of generators and machinery can significantly contribute to noise pollution.
- Airports and Construction Sites: Areas near airports and construction sites often experience high levels of noise pollution.
Health Risks Associated with Noise Pollution:
- Hearing Impairment: Prolonged exposure to loud noises can damage hair cells in the ear, leading to hearing loss.
- Cardiovascular Problems: Exposure to noise during sleep can increase the risk of heart disease by 5% to 10%.
- Stress and Fatigue: Noise pollution can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to stress, fatigue, and other related health issues.
Prevention Measures:
- Use Earplugs or Earmuffs: When engaging in loud activities or living in noisy areas, use earplugs or earmuffs to reduce noise exposure.
- Reduce Generator Use: Limiting generator use can help minimize noise pollution.
- Implement Noise Control Measures: Governments and individuals can work together to enforce noise control measures and promote soundproofing in public and private spaces.
Source: Nairametrics